First Law of Thermodynamics
- Admin

- Jul 19, 2020
- 2 min read
Updated: Jul 22, 2020
We know that as per law of conservation of energy, energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but can be converted from one form to other form. 1st law of thermodynamics is the slight modification of law of conservation of energy and can be stated as;
Heat and work are mutually convertible to each other during any change of state.
1st law for cycle and simple process may be discussed differently.
1st Law of Thermodynamics for cyclic process
For a cyclic process 1st law of thermodynamics states that during any change of state when initial and final condition are same then total heat transfer will be equal to total work transfer.
Joule’s Experiment
In Joule’s Experiment, an adiabatic vessel consist of a known mass of water having thermometer and a stirrer. The water is stirred up by a system of paddles and is operated by a system of following weights. The amount of water done in a system results in the rise of temperature of water.
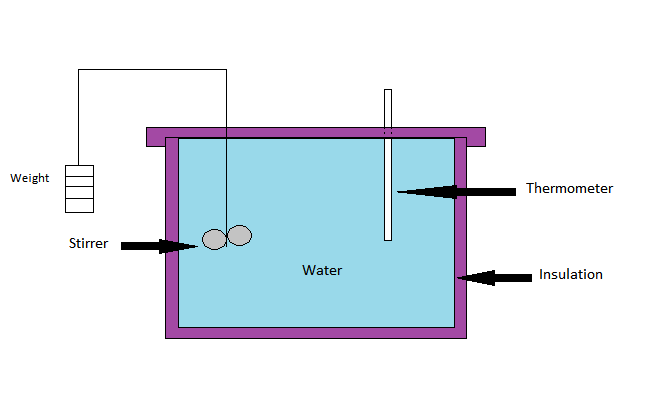
The work can be measured by the product of weight and distance through which it fall.
Let the system is initially at temperature T₁ measured by thermometer which is same as that of atmosphere.
After work temperature rises to T₂ at same pressure i.e one atmosphere. Now as per Joule’s law if transfer of heat and work takes place across boundary of system in cyclic process. Then the net work transfer is equal to net heat transfer.
∮ dW = ∮ dQ
dW = work done
dQ = heat change or temp. change
1st law of thermodynamics for change of state
As per 1st law of thermodynamics for a cycle, the net heat interaction is equal to net work interaction but this is not applicable in case of simple process. During any change of state the net energy interaction is accumulated in the system. As per first law if a system is undergoing a change of state in which heat interaction is involved the remaining energy which is not transferred, is stored within the system and is called internal energy.
Q₁₋₂ – W₁₋₂ = dU₁₋₂
Q₁₋₂ = dU₁₋₂ + W₁₋₂
Where 1-2 is the initial and final conditions during change of state.
Joule’s Law
As per this law change in internal energy during any change of state is directly proportional to temperature difference during the same change of state.
Let a system is going from state 1-2 then as Joule’s Law
dU₁₋₂ ∝ dT₁₋₂
dU₁₋₂ = mC𝗏dT₁₋₂
where C𝗏 = Specific heat at constant volume
m = mass
as internal energy is the property of system. Therefore change of internal energy should be point function.

Comments